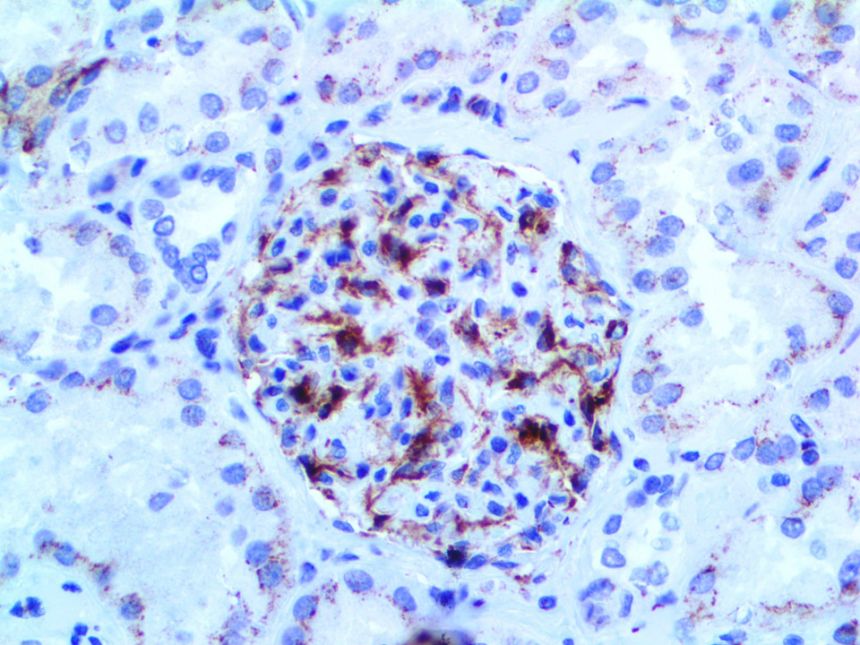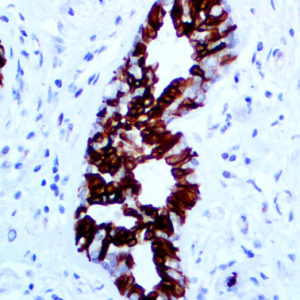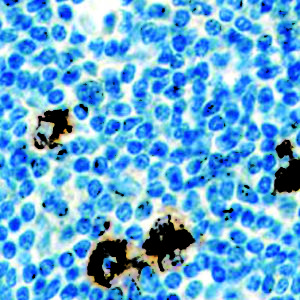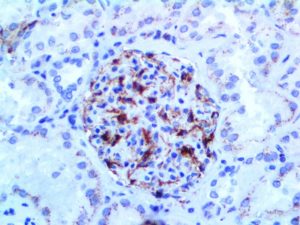
IHC of VEGF on an FFPE Kidney Tissue
| Intended Use | For In Vitro Diagnostic Use | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary and Explanation | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis (the de novo formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). As its name implies, VEGF activity is restricted mainly to cells of the vascular endothelium, although it has an effect on a limited number of other cell types (e.g., stimulation monocyte/macrophage migration). VEGF has been implicated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. The overexpression of VEGF may be an early step in the process of metastasis, a step involved in the “angiogenic” switch. Although VEGF has been correlated with poor survival, its exact mechanism of action in the progression of tumors remains unclear. VEGF is also released in rheumatoid arthritis in response to TNF-alpha, increasing endothelial permeability and swelling and also stimulating angiogenesis (formation of capillaries). Once released, VEGF may elicit several responses. It may cause a cell to survive, move, or further differentiate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibody Type | Rabbit Monoclonal | Clone | RBT-VEGF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotype | IgG | Reactivity | Paraffin, Frozen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Localization | Cytoplasmic, Cell Surface | Control | Placenta, Angiosarcoma, Angioma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Presentation | VEGF is a rabbit monoclonal antibody derived from cell culture supernatant that is concentrated, dialyzed, filter sterilized and diluted in buffer pH 7.5, containing BSA and sodium azide as a preservative. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Availability |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: For concentrated antibodies, please centrifuge prior to use to ensure recovery of all product. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||