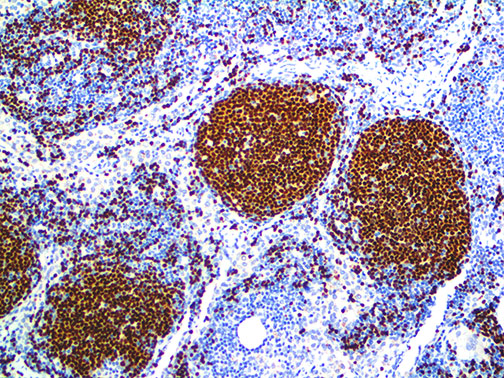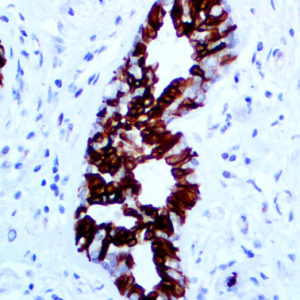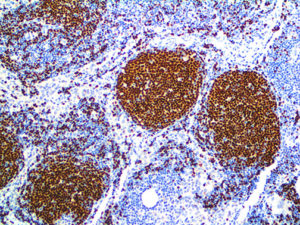
IHC of PAX-5 on an FFPE Tonsil Tissue
| Intended Use | For In Vitro Diagnostic Use | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary and Explanation | The PAX proteins are important regulators in early development, and alterations in the expression of their genes are thought to contribute to neoplastic transformation. The PAX-5 gene encodes the B-cell lineagespecific activator protein (BSAP) that is expressed at early, but not late, stages of B-cell differentiation. Its expression has also been detected in developing CNS and testis; therefore, PAX-5 gene product may not only play an important role in B-cell differentiation, but also in neural development and spermatogenesis. PAX-5 expression is not only continuously required for B-cell lineage commitment during early B-cell development but also for B-cell lineage maintenance. PAX-5 is found in most cases of mature and precursor B-cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas/Leukemias. PAX-5 is not detected in Multiple Myeloma and solitary Plasmacytoma, making it useful for such differentiation. Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas do express PAX-5, except for those with terminal B-cell differentiation. T-cell neoplasms do not stain with anti-PAX-5; however, there is a strong association with CD20 expression. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibody Type | Rabbit Monoclonal | Clone | RBT-PAX5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotype | IgG | Reactivity | Paraffin, Frozen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Localization | Nuclear | Control | Tonsil, Lymph Node, Spleen, Thymus, Colon, Liver, Lymphoblastic Lymphoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Presentation | PAX-5 is a rabbit monoclonal antibody derived from cell culture supernatant that is concentrated, dialyzed, filter sterilized and diluted in buffer pH 7.5, containing BSA and sodium azide as a preservative. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Availability |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: For concentrated antibodies, please centrifuge prior to use to ensure recovery of all product. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||