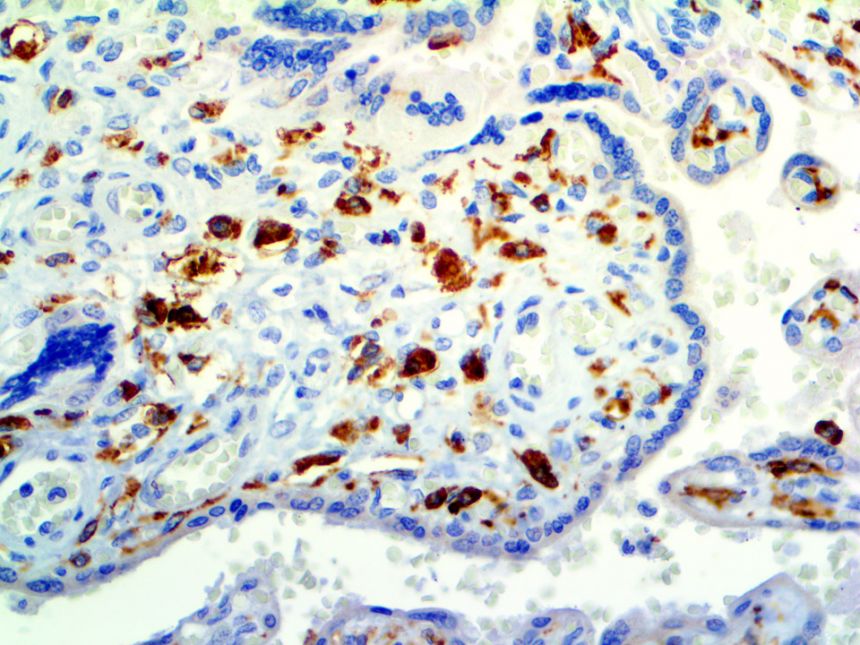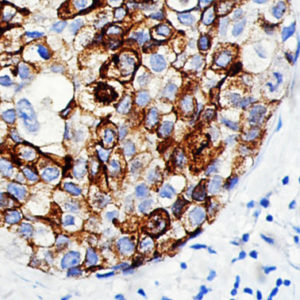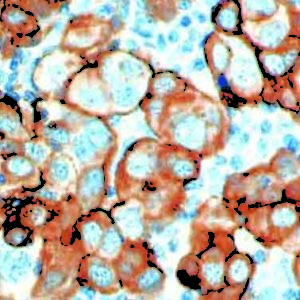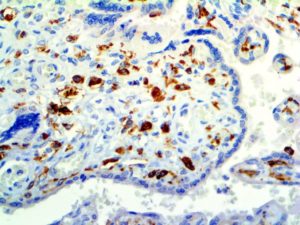
IHC of CD14 on an FFPE Placenta Tissue
| Intended Use | For In Vitro Diagnostic Use | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary and Explanation | CD14 is a component of the innate immune system. CD14 exists in two forms: mCD14 (anchored by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail) or sCD14 (soluble). CD14 acts as a co-receptor (along with the Toll-like receptor TLR 4 and MD-2) for the detection of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). CD14 can only bind LPS in the presence of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP). Although LPS is considered it’s main ligand, CD14 also recognizes other pathogen associated molecular patterns. CD14 is expressed mainly by macrophages and (at 10 times lesser extent) by neutrophil granulocytes. A soluble form sCD14 is secreted by the liver and monocytes and is sufficient in low concentrations to confer LPS-responsiveness to cells which otherwise do not express CD14. sCD14 is also present in human milk where it is believed to regulate microbial growth in the infant gut. Increased sCD14 levels are associated with inflammatory infectious diseases and high mortality in gram-negative shock. CD14 also appears to be involved in clearance of gram-negative bacteria via its high affinity binding to LPS-LPB complexes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibody Type | Rabbit Monoclonal | Clone | EP128 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotype | IgG | Reactivity | Paraffin, Frozen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Localization | Cytoplasmic, Membranous | Control | Placenta, Tonsil, Spleen, Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Presentation | CD14 is a rabbit monoclonal antibody derived from cell culture supernatant that is concentrated, dialyzed, filter sterilized and diluted in buffer pH 7.5, containing BSA and sodium azide as a preservative. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Availability |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: For concentrated antibodies, please centrifuge prior to use to ensure recovery of all product. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||