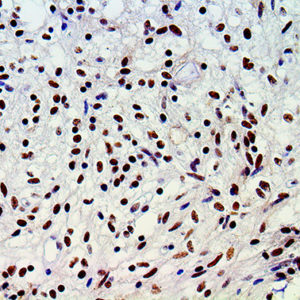
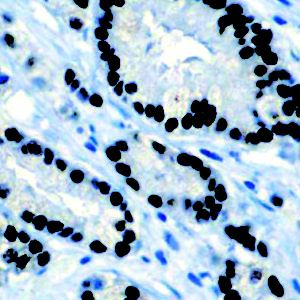
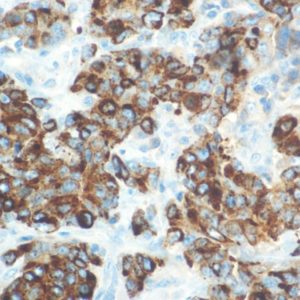
IHC of Amyloid A on a FFPE Kidney Tissue
| Intended Use | For In Vitro Diagnostic Use | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary and Explanation | Serum amyloid A (SAA) proteins are a family of apolipoproteins associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in plasma. Different isoforms of SAA are expressed constitutively (constitutive SAAs) at different levels or in response to inflammatory stimuli (acute phase SAAs). These proteins are produced predominantly by the liver. The conservation of these proteins throughout invertebrates and vertebrates suggests that SAAs play a highly essential role in all animals. Acute-phase serum amyloid A proteins (A-SAAs) are secreted during the acute phase of inflammation. These proteins have several roles, including the transport of cholesterol to the liver for secretion into the bile, the recruitment of immune cells to inflammatory sites, and the induction of enzymes that degrade extracellular matrix. A-SAAs are implicated in several chronic inflammatory diseases, such as amyloidosis, atherosclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Amyloidosis is a disease characterized by the abnormal build-up of amyloid, abnormal non-branching fibrillary β-pleated sheet proteins that are insoluble and highly resistant to proteolytic degradation that result in localized or systemic organ dysfunction. Amyloidosis are grouped as AL (primary), AA (secondary), and hereditary forms. Proper classification is important since treatment and prognosis of the disorders are vastly different. AA amyloidosis is associated with a variety of chronic inflammatory conditions and infections, derived from SAA. Immunohistochemical staining using a panel of antibodies including κ and λ Ig light chains, Amyloid A, and Transthyretin can aid in recognizing most forms of amyloid. The Amyloid A immunostaining detects tissue deposition of serum Amyloid A protein, an acute phase reactive protein. It is positive in AA Amyloidosis and familial Mediterranean fever. Recently, SAA has also been investigated as a potential marker for neoplastic activity. SAA concentrations have been reported to be a marker of poor prognosis, elevated in patients with advanced stages of cancer and those with malignant disease. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibody Type | Rabbit Monoclonal | Clone | EP335 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotype | IgG | Reactivity | Paraffin, Frozen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Localization | Extracellular, Cytoplasmic | Control | Kidney, Amyloidosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Presentation | Amyloid A is a rabbit monoclonal antibody derived from cell culture supernatant that is concentrated, dialyzed, filter sterilized and diluted in buffer pH 7.5, containing BSA and sodium azide as a preservative. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Availability |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: For concentrated antibodies, please centrifuge prior to use to ensure recovery of all product. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||